Unlock the secrets of alcohol metabolism and discover why that third beer can have you feeling tipsy in no time.
Table of Contents
Who hasn’t wondered at some point, “How many beers does it take to get drunk?” It’s a common question with a complex answer that delves into the science behind alcohol metabolism, individual tolerance levels, and various factors influencing intoxication. To truly understand this phenomenon, we must explore the intricacies of alcohol consumption and its effects on the body.
Factors Influencing Alcohol Intoxication
Alcohol metabolism plays a crucial role in determining how quickly and intensely someone becomes intoxicated. When we drink, alcohol is absorbed into the bloodstream and metabolized by the liver. Blood Alcohol Content (BAC) is a measure of the amount of alcohol in the bloodstream and is used to gauge intoxication levels. Factors such as gender, body weight, and rate of consumption all influence how alcohol is processed in the body.
Gender differences impact alcohol tolerance, with women generally metabolizing alcohol slower than men due to differences in body composition and enzyme levels. This means that a woman may feel the effects of alcohol more quickly than a man, even if they consume the same amount of alcohol.
Body weight and composition also play a role in alcohol tolerance. Individuals with higher body weight tend to have more body water, which can help dilute alcohol and reduce its effects. Conversely, individuals with lower body weight may feel the effects of alcohol more intensely due to higher BAC levels.
The rate of alcohol consumption and absorption can significantly impact intoxication levels. Consuming alcohol quickly can lead to a rapid increase in BAC, increasing the likelihood of feeling drunk. Slowing down the pace of drinking and allowing time for alcohol to be metabolized can help manage intoxication levels.
Individual Variations in Alcohol Tolerance
While there are general guidelines for alcohol consumption, individual variations in alcohol tolerance can significantly impact how someone responds to alcohol. Genetic factors play a role in alcohol sensitivity, with some individuals genetically predisposed to metabolize alcohol more efficiently. Enzyme deficiencies, such as a lack of certain enzymes needed to break down alcohol, can also affect how quickly someone becomes intoxicated.
Alcohol sensitivity varies from person to person, with some individuals more sensitive to the effects of alcohol than others. This can be influenced by factors such as age, overall health, and previous experience with alcohol consumption. Someone with a higher tolerance for alcohol may need to consume more drinks to feel intoxicated compared to someone with lower tolerance.
Experience with alcohol consumption can impact tolerance levels. Regular drinkers may develop a higher tolerance for alcohol over time, requiring more drinks to achieve the same level of intoxication. Occasional drinkers or individuals with little to no experience with alcohol may feel the effects more quickly with fewer drinks.
Tips for Responsible Drinking and Avoiding Intoxication
Understanding your own limits when it comes to alcohol consumption is essential for responsible drinking. Knowing how your body responds to alcohol and being mindful of your tolerance levels can help prevent overconsumption and potential risks associated with intoxication.
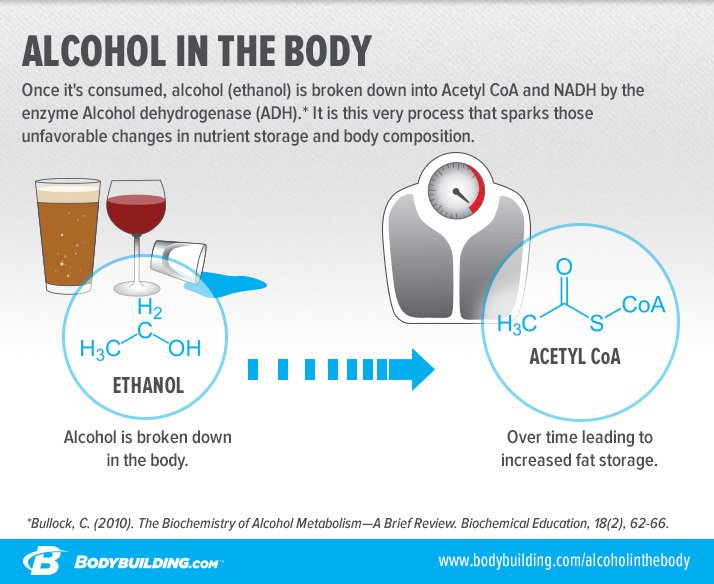
Image courtesy of www.bodybuilding.com via Google Images
Alternating alcoholic drinks with non-alcoholic beverages can help moderate alcohol intake and give your body time to process the alcohol. Drinking water between alcoholic beverages can help stay hydrated and reduce the chances of feeling the effects of alcohol more intensely.
Eating before and during drinking can also help slow down the absorption of alcohol and reduce the likelihood of becoming drunk quickly. Consuming food high in protein and complex carbohydrates can help absorb alcohol and lessen its effects on the body.
Planning safe transportation before drinking is crucial to ensure a responsible night out. Having a designated driver, using public transportation, or calling a rideshare service can help avoid the dangers of driving under the influence.
Closing Thoughts
As we navigate the complex world of alcohol consumption, it’s important to remember the science behind how our bodies metabolize alcohol and respond to intoxication. Understanding the factors influencing alcohol tolerance and the individual variations in how we process alcohol can help us make informed decisions about responsible drinking.
By knowing our limits, practicing moderation, and planning ahead for safe transportation, we can enjoy the social aspects of alcohol consumption while minimizing the risks associated with intoxication. So the next time you ask yourself, “How many beers does it take to get drunk?” remember to drink responsibly and prioritize your well-being above all else.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does alcohol metabolism vary between individuals?
Alcohol metabolism can vary based on factors such as gender, body weight, genetic predispositions, enzyme levels, and experience with alcohol consumption. These variations can impact how quickly someone becomes intoxicated and their overall tolerance for alcohol.
What can I do to improve my alcohol tolerance?
To improve alcohol tolerance, consider factors such as body weight, overall health, and previous experience with alcohol. Consuming alcohol in moderation, staying hydrated, and eating before and during drinking can help manage intoxication levels and promote responsible drinking.
How can I tell if I’ve had too much to drink?
Signs that you may have had too much to drink include impaired coordination, slurred speech, decreased inhibitions, and memory lapses. Monitoring your alcohol intake, knowing your limits, and recognizing these signs can help prevent overconsumption and potential risks associated with intoxication.
Is it safe to drive after drinking alcohol?
It is not safe to drive after drinking alcohol. Alcohol can impair judgment, coordination, and reaction time, increasing the risk of accidents and endangering yourself and others on the road. Plan ahead for safe transportation, such as using a designated driver, public transportation, or rideshare services, to avoid driving under the influence.
Generated by Texta.ai Blog Automation


Leave a Reply